Determination of the ridge gene in the Rhodesian Ridgeback
The ridge – the distinctive ridge running against the direction of the coat – is one of the characteristic features of the Rhodesian Ridgeback breed. The appearance of the Ridge is clearly defined by the respective breed standards.
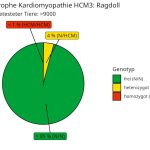
The development of the ridge is caused by a genetic variant on chromosome 18. This is a duplication of an approx. 100 kb long DNA section. The variant follows an autosomal dominant inheritance with incomplete penetrance: in heterozygous dogs with the R/r genotype, around 95% carry a ridge, while in around 5% of dogs the dominant R allele is silenced, meaning that these dogs do not have a ridge.
The genetic test can be used to determine whether the ridge gene is heterozygous (R/r) or homozygous (R/R). The genotypes of the mating partners can be used to predict whether puppies without a ridge can be expected in the offspring.
Our tip: We also offer a new practical Ridge + Dermoidsinus (DS) combination package!