DLA-kirjoitus
- Home
- DLA-kirjoitus
DLA-määritys koirilla
Pyyntömme sinulle: Näytemateriaalina voidaan käyttää vain 0,5 – 1,0 ml EDTA-verta tai erityistä pyyhkäisyä, ei kuivia poskipyyhkäisypyyhkeitä vakiotestipakkauksessamme.
Yleiskatsaus
DLA-geenit koodaavat proteiineja, joilla on keskeinen rooli koiran immuunivasteessa, sillä ne esittävät antigeenejä solujen pinnoilla ja mahdollistavat näin immuunijärjestelmän tunnistaa kehon omat ja vieraat rakenteet. Osana MHC-kompleksia ne periytyvät kiinteinä yhdistelminä (haplotyyppeinä). Näiden geenien suuri geneettinen monimuotoisuus vahvistaa immuunivastetta.
DLA-geenit ja niiden merkitys koiranjalostuksessa
Mitä ovat DLA-geenit?
Niin sanotut DLA-geenit (dog leukosyyttiantigeeni) koodaavat proteiineja, joilla on keskeinen rooli koiran immuunivasteessa. Ne kuuluvat niin sanottuun II luokan MHC-kompleksiin (major histocompatibility complex), jonka tehtävänä on tunnistaa vieraat aineet ja esittää ne immuunijärjestelmälle, jotta se voi käynnistää kohdennetun puolustusreaktion. Erottelu elimistön omien ja vieraiden solujen (kuten bakteerien tai virusten) välillä on olennaisen tärkeää, ja virheet tässä voivat johtaa autoimmuunisairauksiin.
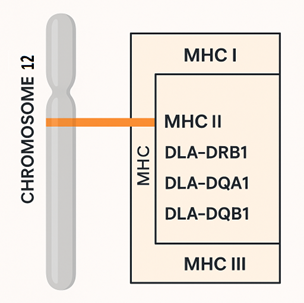
Koirilla MHC-kompleksi sijaitsee kromosomissa 12. Kasvattajien ja eläinlääkäreiden kannalta erityisen tärkeät DLA-geenit sijaitsevat luokan II alueella, joka vastaa niin sanotun humoraalisen (vasta-ainevälitteisen) immuunivasteen hallinnasta.
Kolme tärkeintä DLA-geeniä, joita analysoidaan koiranjalostuksessa, ovat:
– DLA-DRB1
– DLA-DQA1
– DLA-DQB1 – DLA-DQB1
Nämä geenit toimivat yhdessä ja periytyvät haplotyyppinä – eli ne periytyvät kiinteänä yhdistelmänä vanhemmilta jälkeläisille.
Miksi DLA-geenit ovat tärkeitä?
DLA-geenien suuri monimuotoisuus edistää vakaata ja toimivaa immuunijärjestelmää. Mitä suurempi geneettinen monimuotoisuus on, sitä paremmin immuunijärjestelmä pystyy puolustautumaan erilaisia taudinaiheuttajia vastaan.
Monissa koiraroduissa on vain pieni määrä mahdollisia haplotyyppejä, koska valikoiva jalostus on vähentänyt monimuotoisuutta. Pieni määrä jalostuskoiria, suosittujen isien käyttö (suosikkikoirien usein toistuva käyttö) tai sukulaiskoirien toistuva astuttaminen voivat rajoittaa tätä monimuotoisuutta huomattavasti, mikä voi vaikuttaa autoimmuunisairauksien riskiin.
Jalostuksen tavoite: DLA-lajin monimuotoisuuden säilyttäminen tai lisääminen rodun sisällä.
Homotsygoottius vs. heterotsygoottius
Homotsygootti: kaksi identtistä geenin alleelia.
Heterotsygootti: geenin kaksi eri alleelia.
Heterotsygoottisella koiralla on siis enemmän geneettistä monimuotoisuutta MHC-kompleksissa kuin homotsygoottisella koiralla, ja sen immuunijärjestelmä on mahdollisesti vahvempi.
Yhteys sairauksiin
Autoimmuunikomponentista keskustellaan tunnettujen sairauksien, kuten diabetes mellituksen, eksokriinisen haiman vajaatoiminnan, kilpirauhasen vajaatoiminnan ja Addisonin taudin, kehittymisen yhteydessä. Tieteelliset tutkimukset ovat yhdistäneet tietyt DLA-haplotyypit lisääntyneeseen tai vähentyneeseen autoimmuunisairauksien riskiin. Sovelletaan seuraavaa:
- Tulos osoittaa lisääntynyttä tai vähentynyttä tautiriskiä.
- Muut ympäristö- ja geneettiset tekijät vaikuttavat taudin puhkeamiseen.
- Se ei ole taudin suora syy.
Esimerkkejä suojaavien alleelien yhdistelmistä
| DLA-DRB1 | DLA-DQA1 | DLA-DQB1 | Vähentynyt riski |
|---|---|---|---|
| 015:01 | 006:01 | 020:02 | Diabetes mellitus |
| 018:01 | 001:01 | 008:02 | Kilpirauhasen vajaatoiminta |
| 018:01 | 001:01 | 002:01 | Addisonin tauti |
Esimerkkejä riskialleeliyhdistelmistä
| DLA-DRB1 | DLA-DQA1 | DLA-DQB1 | Lisääntynyt riski |
|---|---|---|---|
| 020:01 | 004:01 | 013:03 | Diabetes mellitus |
| 001:01 | 001:01 | 002:01 | Kilpirauhasen vajaatoiminta |
| 001:01 | 002:01 | 013:03 | Addisonin tauti |

Yksi esimerkki:
Englannin cockerspanielilla ”Henri” on geeniyhdistelmä DRB1 001:01 – DQA1 002:01 – DQB1 013:03, johon liittyy lisääntynyt Addisonin taudin riski. Varotoimenpiteenä suositellaan vuosittaista tarkastusta eläinlääkärillä, johon sisältyy verikoe (esim. Addisonin profiili).
DLA-kirjoittaminen käytännössä
DLA-tyypitys määrittää koiran alleelit. Tämä tehdään sekvensoimalla laboratoriossa ja tekemällä sen jälkeen bioinformatiikan analyysi.
Kirjoittamisen kohderyhmät
- Kasvattajat, jotka haluavat säilyttää populaation geneettisen monimuotoisuuden.
- siitoskoirien omistajat, sopivien kumppaneiden kohdennettua valintaa varten.
- uhanalaisten rotujen omistajat yksilöllisten terveysriskien arvioimiseksi (tiettyjen alleelien varhaista havaitsemista tai ennaltaehkäisyä varten).
Mitä kirjoitus osoittaa?
✅ Luettelo DLA-DRB1-, DLA-DQA1- ja DLA-DQB1-geenien yksittäisistä alleeleista (esim. DRB1*015:01, DQA1*001:01).
✅ Merkintä lisääntyneestä tai vähentyneestä tautiriskistä, jos se on rodun osalta tiedossa.
❌ Ei suoraa tautien havaitsemista
Jalostusta koskevat suositukset
- Valitse mahdollisimman heterotsygoottisia jalostuseläimiä monimuotoisuuden edistämiseksi.
- Vältä samojen alleelien parittelua heterotsygoottisten jälkeläisten tuottamiseksi.
- Tehdään kartoitus DLA:n monimuotoisuudesta jalostusorganisaatiossa.
- Pitkän aikavälin jalostustavoite: tasapaino geneettisen monimuotoisuuden, rotumääritelmän ja MHC-geenien monimuotoisuuden välillä.
Päätelmä
DLA-geenit ovat keskeinen väline koiran immuunijärjestelmän geneettisen monimuotoisuuden arvioinnissa. Kohdennetun DLA-tyypityksen avulla kasvattajat voivat toimia vastuullisesti ja vähentää terveysriskejä omissa jälkeläisissään ja populaatiossa pitkällä aikavälillä.

